Intermittent fasting (IF) is a dietary approach that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. From a medical perspective, there’s growing interest and research into its potential health benefits. Here’s an overview:

Weight Loss and Metabolic Health:
One of the primary reasons people try intermittent fasting is for weight loss. Several studies suggest that IF can lead to significant weight loss and improvements in metabolic health markers such as insulin sensitivity and cholesterol levels. However, individual responses can vary.
Insulin Sensitivity:
Intermittent fasting may improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for blood sugar regulation. By allowing periods of fasting, it gives the body a break from constantly processing food, potentially reducing insulin resistance.
Cellular Repair and Autophagy:
Fasting triggers autophagy, a process where cells remove dysfunctional components and recycle them for energy. This cellular repair mechanism may have anti-aging effects and could help protect against various diseases.
Inflammation Reduction:
Some studies suggest that intermittent fasting may reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to various health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Heart Health:
IF may have benefits for heart health, such as lowering blood pressure, reducing LDL cholesterol levels, and improving other risk factors for heart disease.
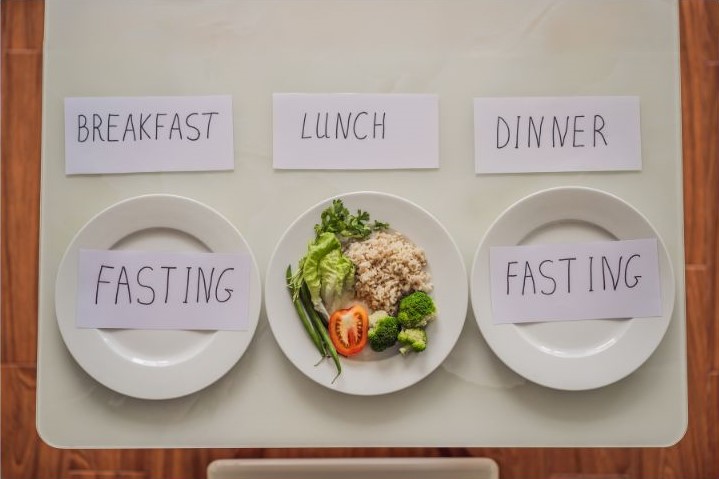
Brain Health:
There’s emerging research suggesting that intermittent fasting may have cognitive benefits. It may promote the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports brain health and cognitive function.
Longevity:
Some animal studies have shown that intermittent fasting can extend lifespan, although more research is needed to understand if this effect translates to humans.
It’s essential to approach intermittent fasting with caution, especially for individuals with certain medical conditions or those who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or underweight. It’s also crucial to maintain proper nutrition during eating periods to ensure you’re getting all the necessary nutrients.
Before starting any fasting regimen, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health issues or are taking medications. They can help tailor an approach that’s safe and suitable for your individual needs.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Let’s Stay In Touch
Let’s Stay In Touch
Subscribe to the Gam-Med’s newsletter to stay in the know of changes, events, new policies and procedures.